|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Legacy applications often sit at the center of critical business operations. But over time, performance slows, integrations break down, and innovation becomes harder to execute.
Application modernization helps organizations extend the value of existing systems while aligning with cloud strategy, security standards, and AI-driven innovation. This FAQ answers the most common questions business and technology leaders ask before starting a modernization initiative.
Q: What is application modernization?
A: Application modernization is the process of updating legacy software applications to improve performance, security, scalability, and user experience. This may include moving to cloud infrastructure, updating architecture or technology stack, improving integrations, or redesigning the interface. The goal is to extend value while aligning the application with current business, compliance, and technology standards.
Learn more about the benefits of application modernization.
Q: What’s the difference between rebuilding, rehosting, and refactoring?
A: Rehosting (“lift and shift”) moves an app to new infrastructure without major code changes. Refactoring restructures existing code to improve performance or scalability. Rebuilding replaces the application entirely with a new architecture. The right approach depends on technical debt, business goals, and long-term strategy.
This app modernization guide really breaks it all down.
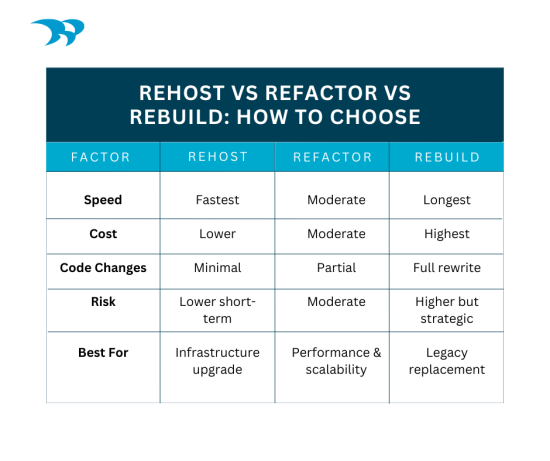
Q: How do you assess whether to modernize or replace an application?
A: Assessment involves reviewing business value, technical debt, architecture, scalability, security posture, and integration complexity. If the core logic still delivers value, refactoring may work. If the architecture is brittle, outdated, or costly to maintain, a rebuild may be more strategic long term. A discovery phase clarifies direction.
Here’s more on what goes into making that decision.
Q: When is the right time to modernize an application?
A: The right time is when performance declines, maintenance costs rise, security risks increase, or the application limits growth. Triggers often include cloud strategy shifts, AI initiatives, compliance updates, vendor end-of-life, difficulty integrating with modern systems, or difficulty finding skilled developers to maintain outdated software.
Here are 3 signs it’s time to modernize your software.
Q: How long does app modernization take?
A: Timelines vary based on complexity, integrations, compliance requirements, and scope. Smaller refactoring projects may take a few months, while full rebuilds can take 6–12 months or longer. A discovery and architecture phase helps define realistic milestones and phased delivery.
Q: How much does app modernization cost?
A: Costs depend on scope, technical debt, integrations, and whether you rehost, refactor, or rebuild. Smaller modernization initiatives may cost tens of thousands, while enterprise rebuilds can reach several hundred thousand or more. A strategic roadmap helps balance upfront investment with long-term operational savings.
Q: What happens if you don’t modernize apps?
A: Outdated applications become harder to maintain, more vulnerable to security risks, and increasingly incompatible with modern systems. Technical debt grows, performance suffers, and innovation slows. Over time, the cost of maintaining legacy systems may exceed the cost of strategic modernization.
Q: How do you modernize apps without disrupting operations?
A: App modernization can be phased using parallel environments, feature toggles, APIs, and incremental releases. A staged rollout reduces risk and allows testing in production-like environments. Strong governance, user training, and clear change management ensure business continuity throughout the transition.
Q: What’s the difference between modernizing a web app and a mobile app?
A: Web app modernization often focuses on cloud architecture, performance, and browser-based UX improvements. Mobile app modernization must address device compatibility, offline capabilities, app store deployment, and native performance. Mobile projects also require stronger API design and backend integration to support real-time user experiences.
Q: Can legacy apps be moved to the cloud?
A: Yes, most legacy applications can be migrated to the cloud using rehosting, refactoring, or partial rebuilding. The right approach depends on architecture and dependencies. Cloud migration improves scalability, resilience, and security, but often requires updating integrations, authentication, and infrastructure to align with modern cloud standards.
Q: How do you modernize apps built on .NET Framework or older Microsoft stacks?
A: Modernization may include upgrading to the latest .NET Framework, migrating to .NET, re-architecting for Azure cloud services, containerizing workloads, and improving API layers. Enhancing DevOps pipelines and integrating modern identity, security, and data services ensures long-term scalability and performance.
Here’s why it’s important to upgrade .NET applications to the newer versions.
Q: How do you modernize apps for AI? Why does architecture matter?
A: AI-ready app modernization requires clean data pipelines, API-first architecture, scalable cloud infrastructure, and strong governance. AI depends on structured, accessible, and trusted data. Without modern architecture, AI integrations become brittle, slow, or insecure. Designing for interoperability and analytics from the start is critical.
See how AI and low-code are redefining app modernization.
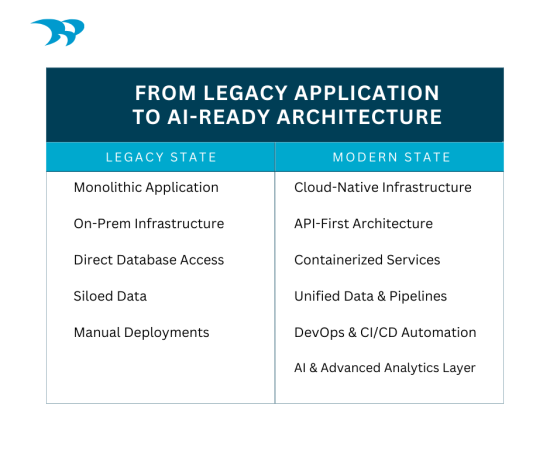
Q: What are the challenges with legacy system integrations?
A: Legacy systems often lack modern APIs, use outdated databases, and have undocumented dependencies. Data inconsistencies, security gaps, and limited scalability create integration risks. Modernization frequently involves building middleware layers, APIs, or data connectors to safely bridge old systems with new platforms.
Q: How do you migrate apps without downtime?
A: Zero-downtime migration uses blue-green deployments, containerization, traffic routing, and staged cutovers. Data is synchronized between environments before switching users to the new system. Automated testing and rollback plans reduce risk and ensure continuity during the transition.
Q: What are the risks of app modernization?
A: Risks include scope creep, integration failures, data migration errors, downtime, and user resistance. Poorly defined requirements or underestimating legacy complexity can increase cost and delays. These risks are mitigated through phased delivery, architectural planning, automated testing, and strong change management practices.
Application modernization isn’t just a technical upgrade. It’s a strategic decision that impacts scalability, security, innovation, and long-term cost. With the right architecture, phased approach, and governance, organizations can modernize confidently without disrupting operations.
If you’re evaluating your next step, a structured discovery and modernization roadmap can clarify risk, investment, and opportunity before you commit to change. Let’s chat.